Mastering Ruby on Rails Active Record Relationships
🚀 Mastering Ruby on Rails Active Record Relationships: The Ultimate Practical Guide
Ruby on Rails shines because of Active Record — a powerful ORM that lets you work with databases like plain Ruby objects. But the real magic happens when you master Active Record Relationships.
In this guide, we’ll explore:
✅ Every major Active Record relationship ✅ Simple explanations + deep insights ✅ Practical examples ✅ Hidden features most developers miss ✅ Unique Active Record powers you should know
Let’s dive in! 💎
🔗 What Are Active Record Relationships?
Active Record relationships define how your models connect with each other in a Rails app.
Think of them as real-world connections:
👉 A user has many posts 👉 A post belongs to a user 👉 A student has many courses through enrollments
Rails provides elegant tools to express these relationships with minimal code.
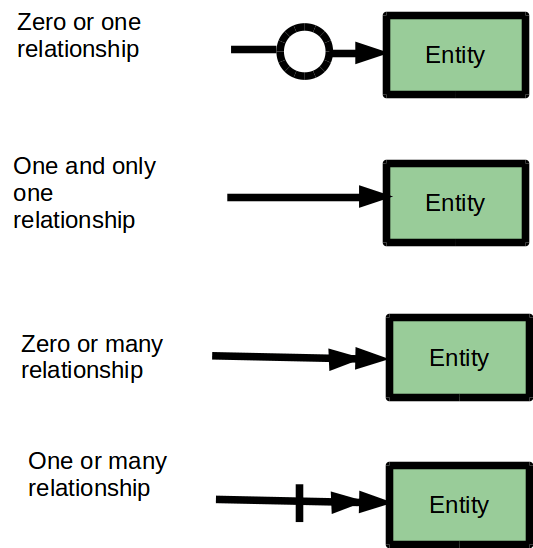
🧩 1. belongs_to Relationship



👉 What it means
A belongs_to relationship indicates that one model is owned by another.
Example
class Post < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :user
end
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_many :posts
end
Each Post belongs to a User.
Usage
post = Post.first
post.user # returns the associated user
⚡ Hidden Features
✅ Optional association
belongs_to :user, optional: true
Useful when foreign key is not mandatory.
✅ Counter cache
belongs_to :user, counter_cache: true
Automatically maintains posts_count in users table.
✅ Touch parent timestamp
belongs_to :user, touch: true
Updates the user’s updated_at when post changes.
🔄 2. has_many Relationship



👉 What it means
A has_many relationship allows one model to be linked to multiple records.
Example
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_many :posts
end
Usage
user.posts
user.posts.create(title: "Rails Magic")
⚡ Hidden Features
✅ Dependent options
has_many :posts, dependent: :destroy
Options include:
:destroy:delete_all:nullify:restrict_with_error
✅ Scopes inside relationships
has_many :published_posts, -> { where(published: true) }, class_name: "Post"
✅ Through association chaining
user.posts.where(created_at: 1.week.ago..Time.now)
🤝 3. has_one Relationship
👉 What it means
A has_one relationship connects one record to exactly one other record.
Example
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_one :profile
end
class Profile < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :user
end
Usage
user.profile
user.create_profile(bio: "Ruby dev")
⚡ Hidden Features
✅ Build association without saving
profile = user.build_profile(bio: "Draft")
✅ Autosave
has_one :profile, autosave: true
Automatically saves associated object.
🔀 4. has_many :through Relationship


👉 What it means
Used for many-to-many relationships with an intermediate model.
Example
class Student < ApplicationRecord
has_many :enrollments
has_many :courses, through: :enrollments
end
class Enrollment < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :student
belongs_to :course
end
Usage
student.courses
student.courses << Course.first
⚡ Hidden Features
✅ Access join attributes
student.enrollments.first.grade
✅ Custom scopes
has_many :active_courses, -> { where(active: true) }, through: :enrollments
🔁 5. has_and_belongs_to_many (HABTM)
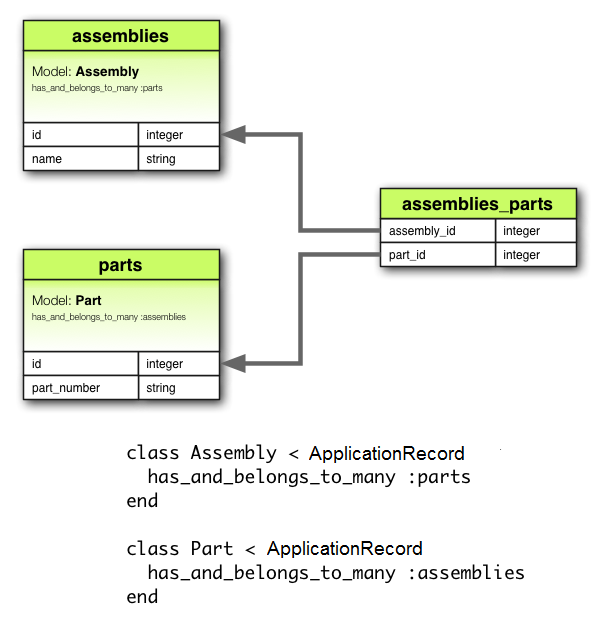


👉 What it means
A simpler many-to-many relationship without a join model.
Example
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :books
end
Requires a join table:
authors_books
⚡ Hidden Features
✅ Faster setup ❌ No extra attributes on join table
👉 Prefer has_many :through for flexibility.
🎯 Advanced Association Features Most Developers Miss
🔍 1. Eager Loading (Performance Boost)
User.includes(:posts)
Prevents N+1 query problems.
🔗 2. Polymorphic Associations
One model can belong to multiple models.
class Comment < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :commentable, polymorphic: true
end
Works with:
Post has_many :comments
Photo has_many :comments
🧠 3. Inverse Associations
Improves performance and memory usage.
has_many :posts, inverse_of: :user
⚙️ 4. Nested Attributes
accepts_nested_attributes_for :posts
Allows creating related records in forms.
✨ Unique & Powerful Active Record Features
Here are some hidden gems 💎:
🚀 1. Query Interface Magic
User.where(active: true).order(:created_at)
Chainable and readable.
🧮 2. Validations + Associations
validates_associated :posts
Ensures associated records are valid.
🔄 3. Callbacks with Relationships
after_create :create_profile
Automates relationship setup.
📊 4. Counter Caches
Instant counts without extra queries.
🧪 5. Dirty Tracking
user.saved_change_to_email?
Detect attribute changes.
🏁 Final Thoughts
Mastering Active Record relationships transforms how you design Rails applications.
When used correctly, they provide:
✅ Clean architecture ✅ Better performance ✅ Maintainable code ✅ Scalable database structure
Quote to remember:
👉 “Good database relationships are the backbone of great Rails applications.”
© Lakhveer Singh Rajput - Blogs. All Rights Reserved.


