Data Science Power Toolkit
🚀 Data Science Power Toolkit: Essential Tools Everyone Should Know 📊🧠
Data Science isn’t just about algorithms — it’s about using the right tools at the right time. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, mastering key data science tools can multiply your productivity and insights.
Let’s explore the must-know data science tools, their features, tricks, working principles, examples, and best use cases 👇
🐍 1. Python — The Backbone of Data Science



✨ Features
- Simple and readable syntax
- Huge ecosystem of libraries (NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn)
- Supports AI, ML, automation, and visualization
- Cross-platform compatibility
⚙️ How It Works
Python acts as a bridge between raw data and analysis. Libraries handle heavy computations and data transformations efficiently.
💡 Tricks
- Use list comprehensions for faster processing
- Leverage vectorized operations with NumPy
- Use virtual environments to manage dependencies
🧪 Example
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("sales.csv")
print(data.groupby("region")["revenue"].mean())
🎯 Best Use Cases
- Machine Learning & AI
- Data cleaning and transformation
- Automation pipelines
- Statistical modeling
📓 2. Jupyter Notebook — Interactive Experiment Lab


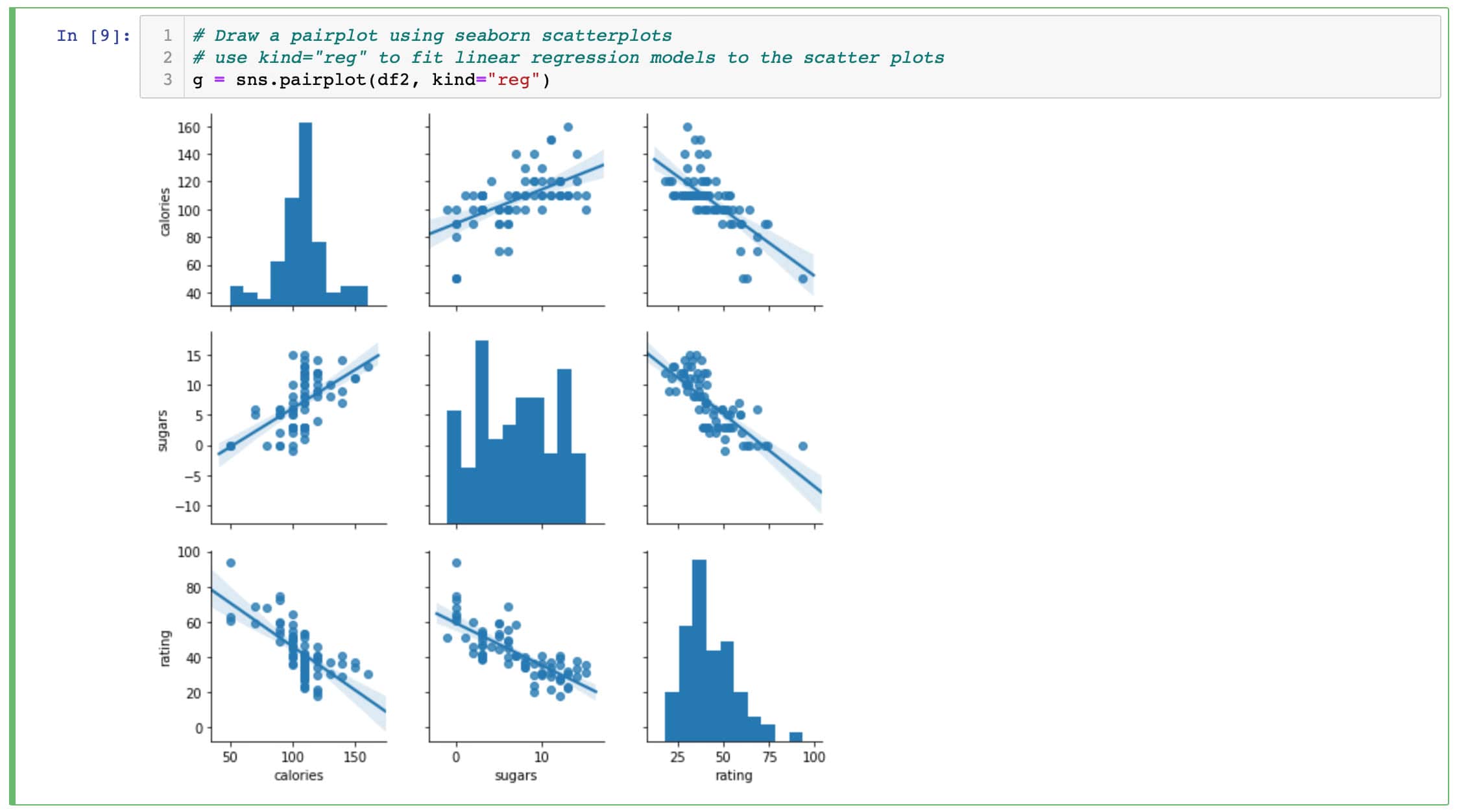
✨ Features
- Interactive code execution
- Inline visualization
- Markdown documentation support
- Ideal for experimentation
⚙️ How It Works
Jupyter runs code in cells, allowing step-by-step execution and real-time feedback.
💡 Tricks
- Use magic commands (
%timeit,%matplotlib inline) - Organize notebooks with markdown headings
- Convert notebooks to scripts or presentations
🧪 Example
%timeit sum(range(10000))
🎯 Best Use Cases
- Data exploration
- Teaching & tutorials
- Rapid prototyping
- Model testing
📊 3. Pandas — Data Manipulation Superpower



✨ Features
- DataFrames for structured data
- Powerful filtering and aggregation
- Handles missing data efficiently
- Fast CSV/Excel processing
⚙️ How It Works
Pandas organizes data into DataFrames (like Excel tables) and enables SQL-like operations.
💡 Tricks
- Use
.locand.ilocfor fast indexing - Chain operations for clean pipelines
- Apply vectorized functions instead of loops
🧪 Example
df = pd.read_csv("employees.csv")
df = df[df["salary"] > 50000]
🎯 Best Use Cases
- Data cleaning
- Feature engineering
- Time-series analysis
- Business analytics
📈 4. Matplotlib & Seaborn — Visualization Masters


✨ Features
- High-quality visualizations
- Statistical plotting
- Customizable styling
- Wide range of chart types
⚙️ How It Works
These libraries convert numerical data into visual insights using plotting APIs.
💡 Tricks
- Use Seaborn for cleaner default styling
- Combine multiple plots for dashboards
- Save figures in high resolution
🧪 Example
import seaborn as sns
sns.histplot(df["age"])
🎯 Best Use Cases
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Reporting & dashboards
- Pattern recognition
🤖 5. Scikit-learn — Machine Learning Engine


✨ Features
- Pre-built ML algorithms
- Model evaluation tools
- Easy API for training models
- Pipeline automation
⚙️ How It Works
Scikit-learn provides a consistent interface for training and evaluating models.
💡 Tricks
- Use pipelines for preprocessing + modeling
- Apply GridSearchCV for tuning
- Normalize data for better performance
🧪 Example
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
🎯 Best Use Cases
- Predictive analytics
- Classification & regression
- Recommendation systems
☁️ 6. SQL — The Language of Data

✨ Features
- Query structured databases
- Fast data retrieval
- Aggregation and joins
- Works with major DB systems
⚙️ How It Works
SQL communicates with relational databases to extract and manipulate data.
💡 Tricks
- Use indexes for performance
- Optimize joins carefully
- Write readable queries
🧪 Example
SELECT region, AVG(sales)
FROM orders
GROUP BY region;
🎯 Best Use Cases
- Business intelligence
- Data warehousing
- Backend analytics
🔥 Final Thoughts: Build Your Data Science Arsenal
The best data scientists don’t just know algorithms — they master tools that turn data into decisions.
👉 Python powers computation 👉 Pandas structures your data 👉 Jupyter accelerates experimentation 👉 Visualization tools reveal patterns 👉 Scikit-learn builds intelligence 👉 SQL connects real-world databases
💬 “Data is the new oil, but tools are the refinery.”
Start small, practice daily, and gradually combine these tools into real-world projects. That’s where true mastery happens 🚀
© Lakhveer Singh Rajput - Blogs. All Rights Reserved.
