Data Models Demystified
🌐 Data Models Demystified: The Blueprint Behind Every Smart Database 🚀
In today’s data-driven world, data models are the invisible architecture that keeps applications organized, scalable, and efficient. Whether you’re building a startup app or a large enterprise system, understanding data models is like learning the grammar of data. 📊
This blog dives deep into types of data models, principles, concepts, terminologies, tools, and real-world examples — all explained simply and clearly. Let’s explore! 👇
🧠 What is a Data Model?
A data model is a conceptual representation of how data is structured, stored, and related in a system. It defines:
✅ Data elements ✅ Relationships between data ✅ Constraints and rules ✅ Storage and retrieval structure
Think of it as a blueprint for databases — just like an architect designs a building before construction. 🏗️
🏗️ Types of Data Models
Data models are broadly categorized into three major levels:
🔹 Conceptual Data Model

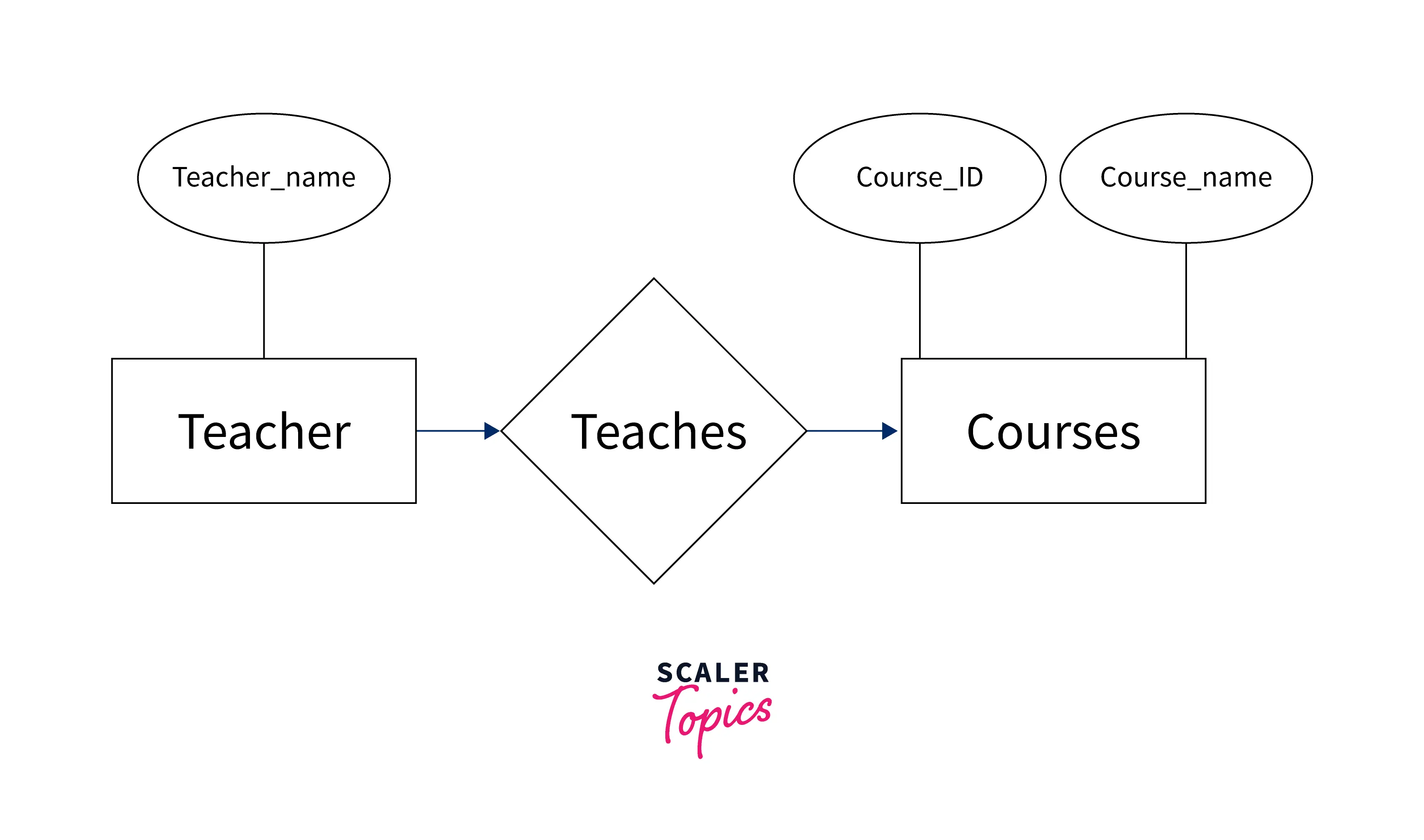
A conceptual data model is a high-level overview of the system. It focuses on what data exists and how entities relate — not technical details.
✨ Features:
- Focuses on entities and relationships
- No database-specific details
- Easy for stakeholders to understand
📌 Example:
A university system with entities:
- Student
- Course
- Professor
Relationships:
- Students enroll in courses
- Professors teach courses
🧩 Tools Used:
- Lucidchart
- Draw.io
- Microsoft Visio
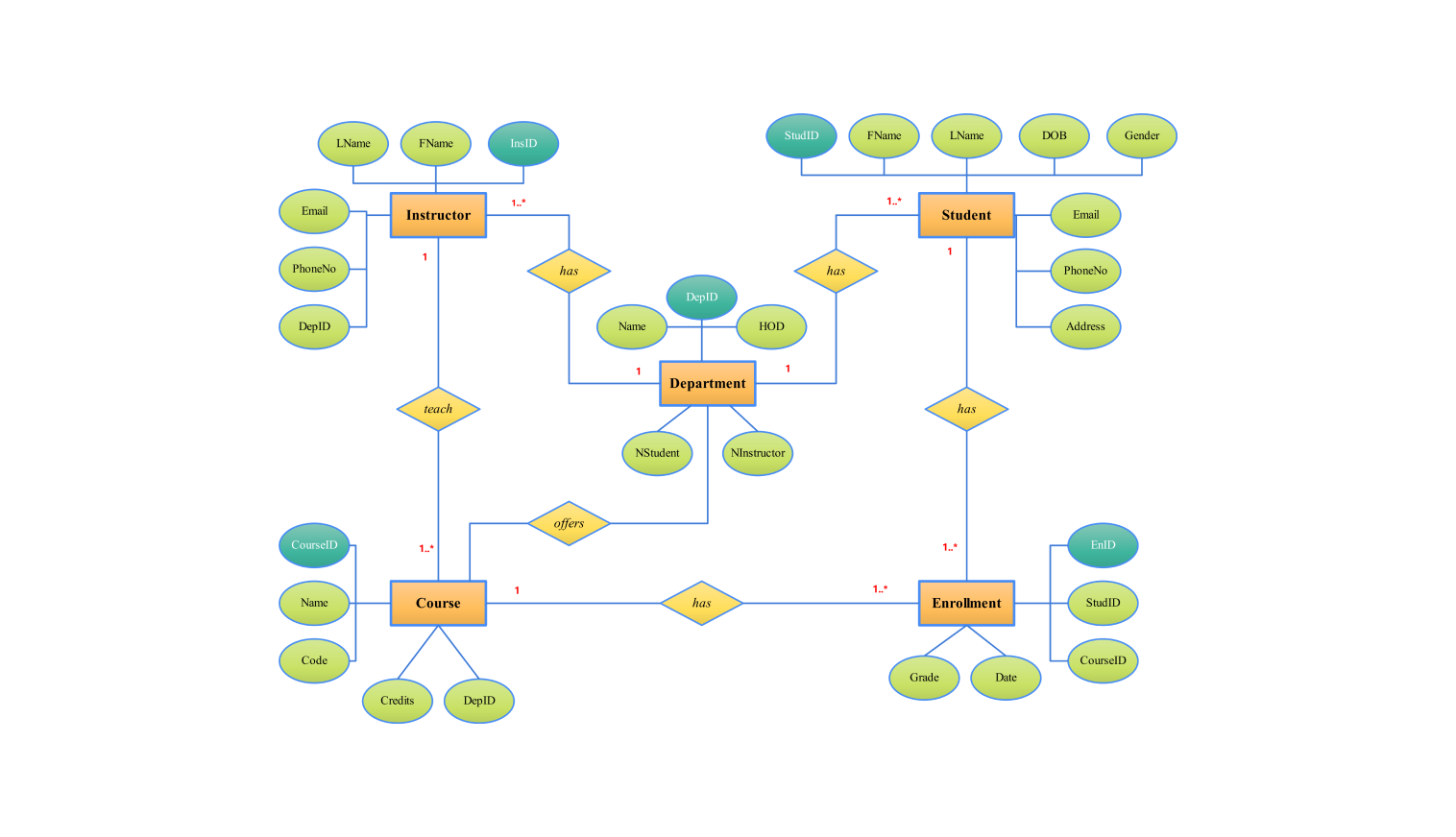
🔹 Logical Data Model


A logical data model adds more structure and detail. It defines attributes, keys, and relationships.
✨ Features:
- Includes fields and data types
- Defines primary and foreign keys
- Normalized structure
📌 Example:
Student table:
Student(ID, Name, Email)
Course table:
Course(ID, Title, Credits)
🧩 Concepts Used:
- Primary Keys 🔑
- Foreign Keys 🔗
- Normalization 📐
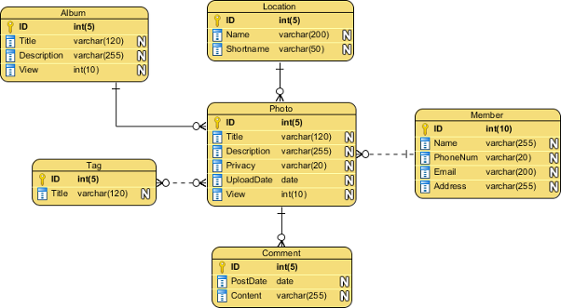
🔹 Physical Data Model



A physical data model represents how data is actually stored in a database.
✨ Features:
- Database-specific implementation
- Indexes and storage details
- Performance optimization
📌 Example (SQL):
CREATE TABLE Students (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
email VARCHAR(255) UNIQUE
);
🧩 Tools Used:
- MySQL Workbench
- pgAdmin
🧩 Types of Database Data Models
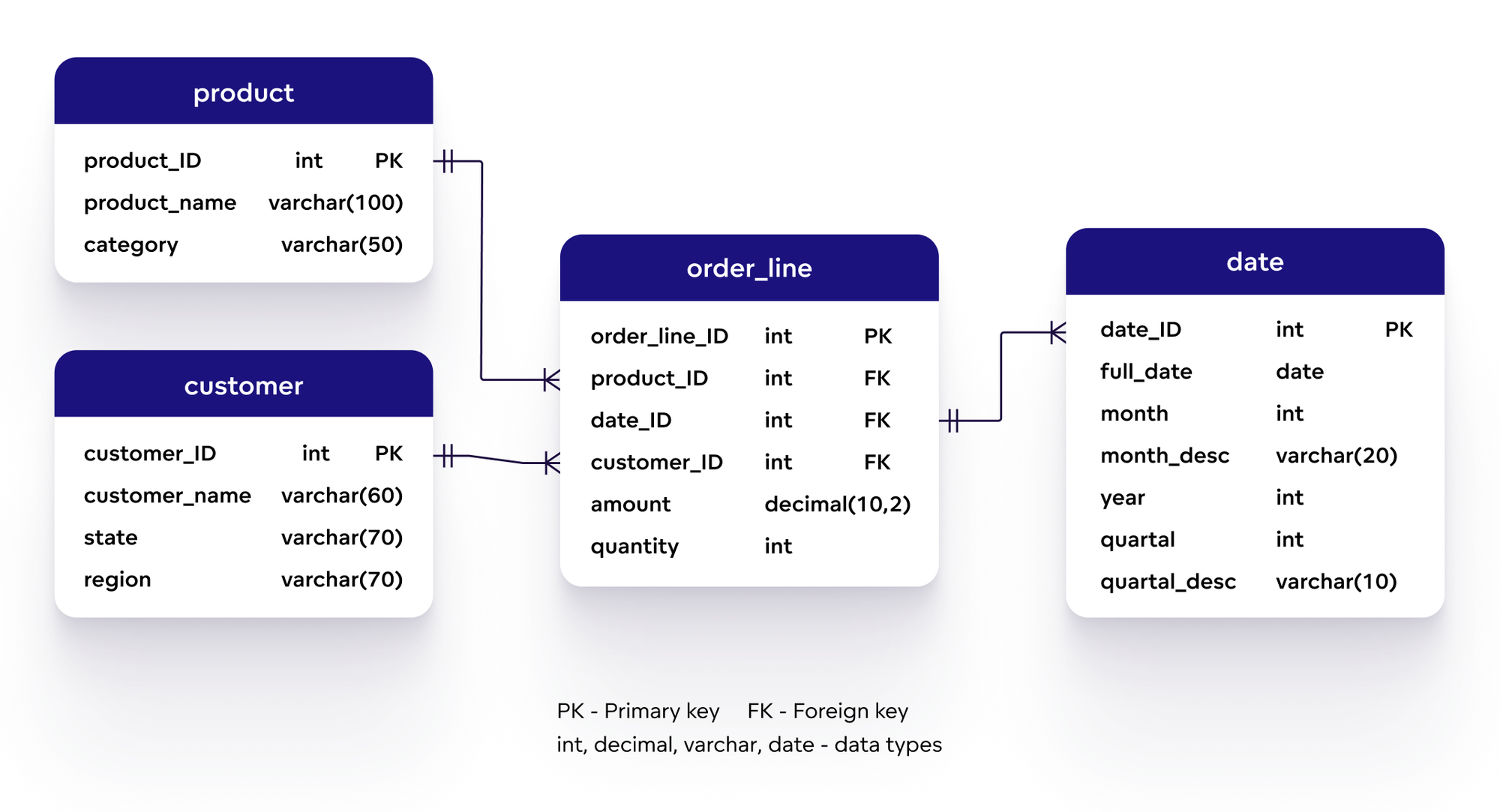
🗂️ Relational Data Model
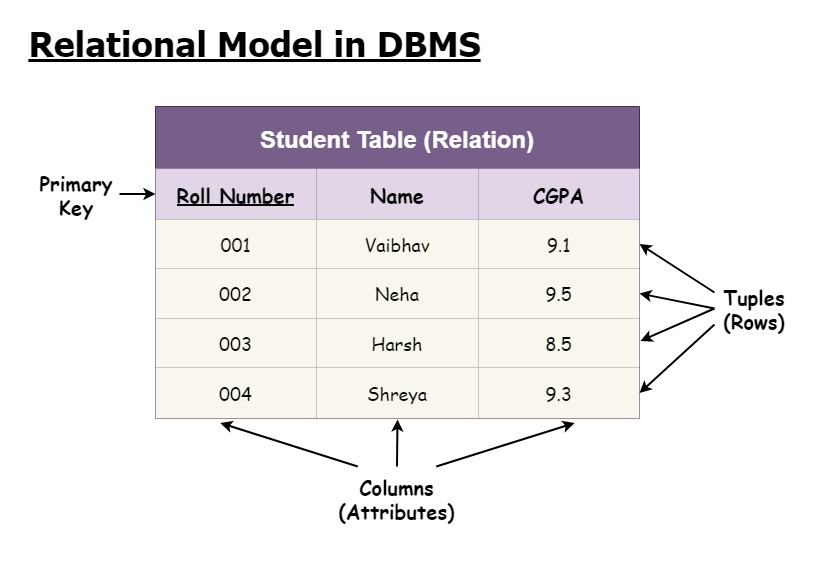
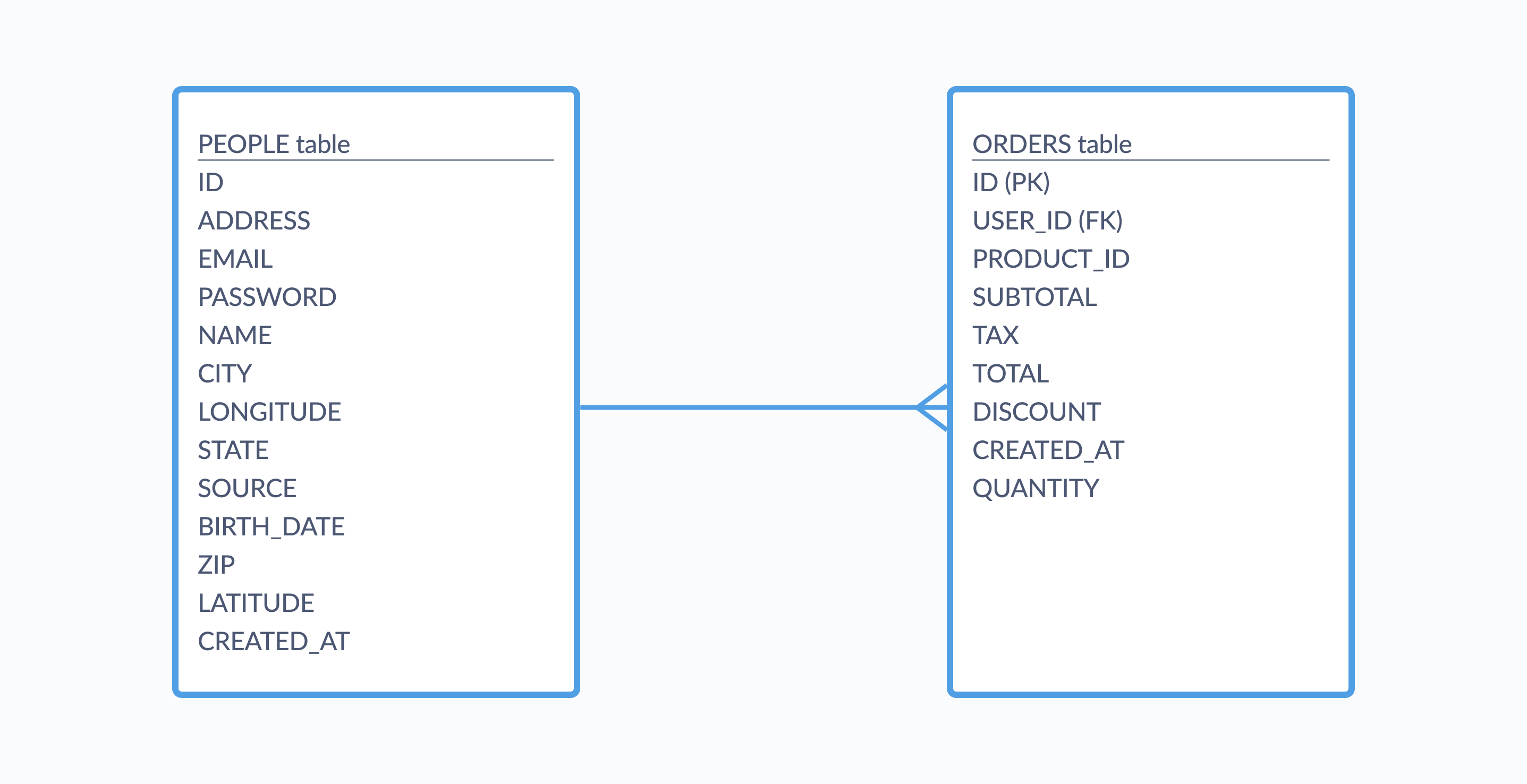
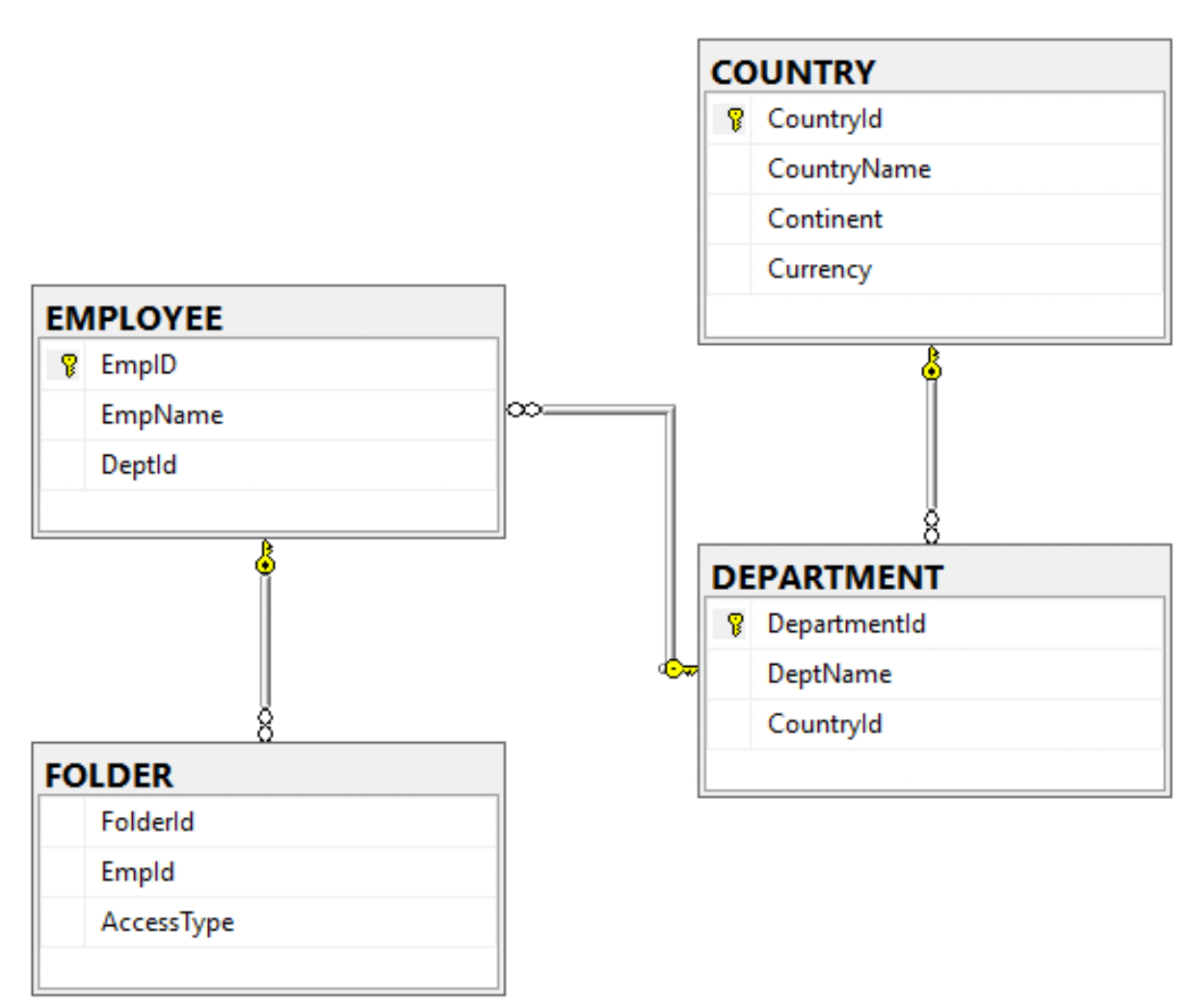
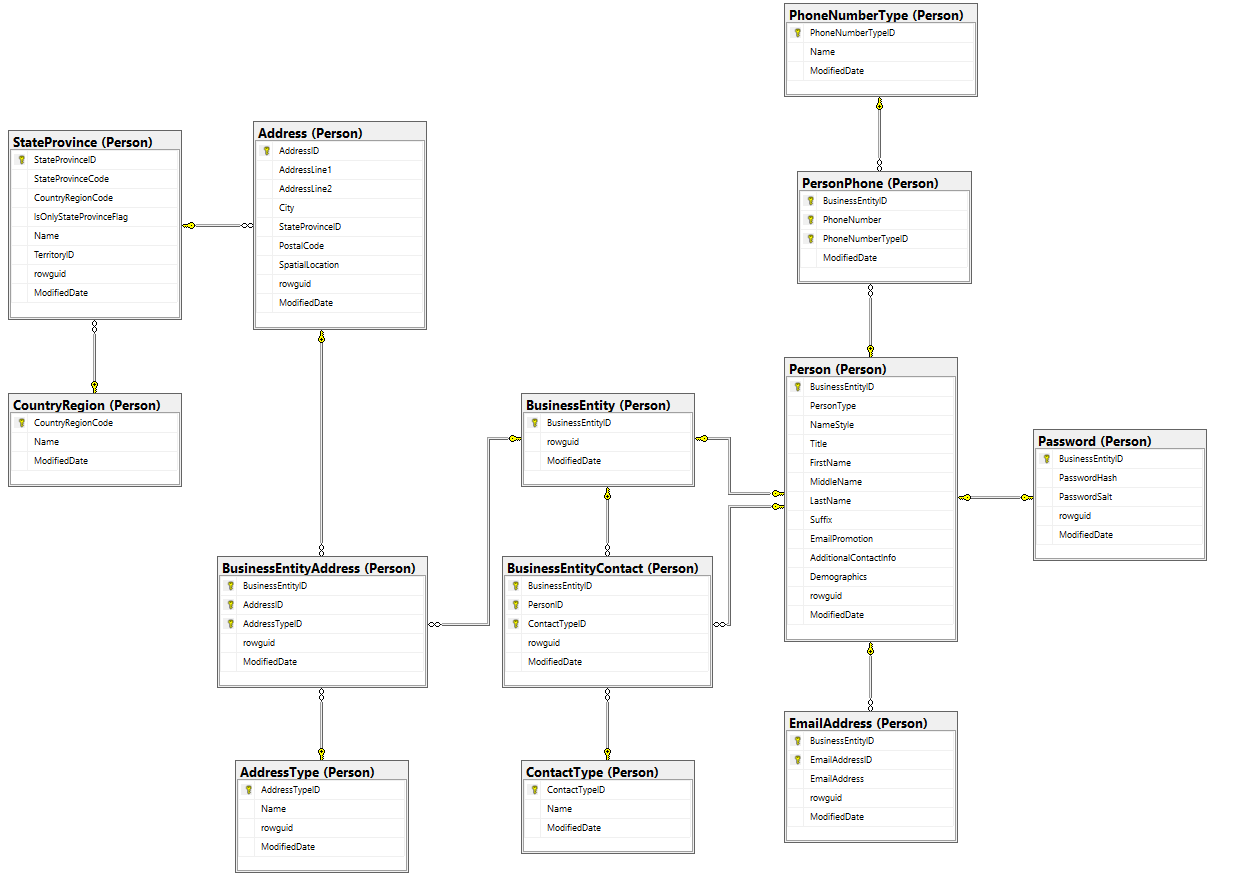
The relational model organizes data into tables with rows and columns.
Popular databases:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- Oracle Database
✨ Features:
- Structured schema
- ACID compliance
- Strong consistency
📌 Use Case:
Banking systems and enterprise apps 💰
🌳 Hierarchical Data Model


Data is organized in a tree-like parent-child structure.
✨ Features:
- One-to-many relationships
- Fast traversal
- Rigid schema
📌 Example:
Company organizational chart 🏢
🕸️ Network Data Model
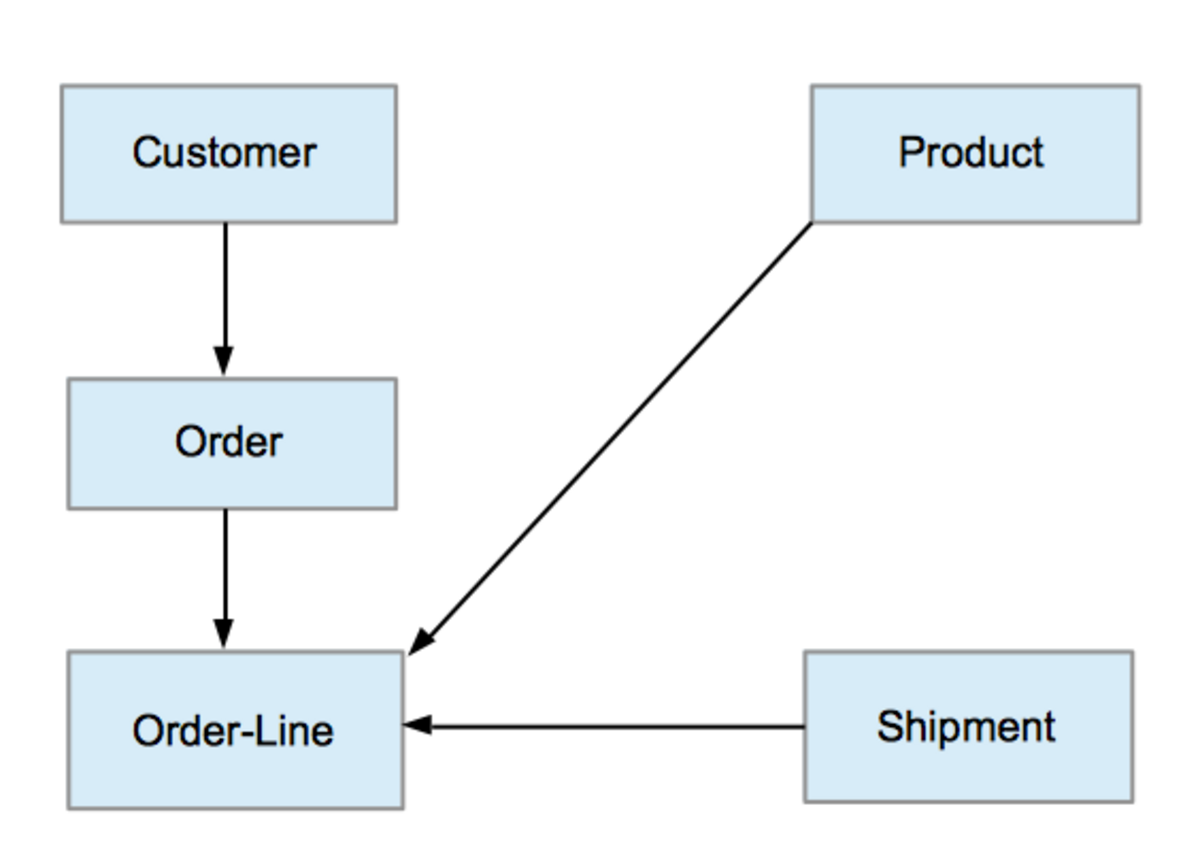

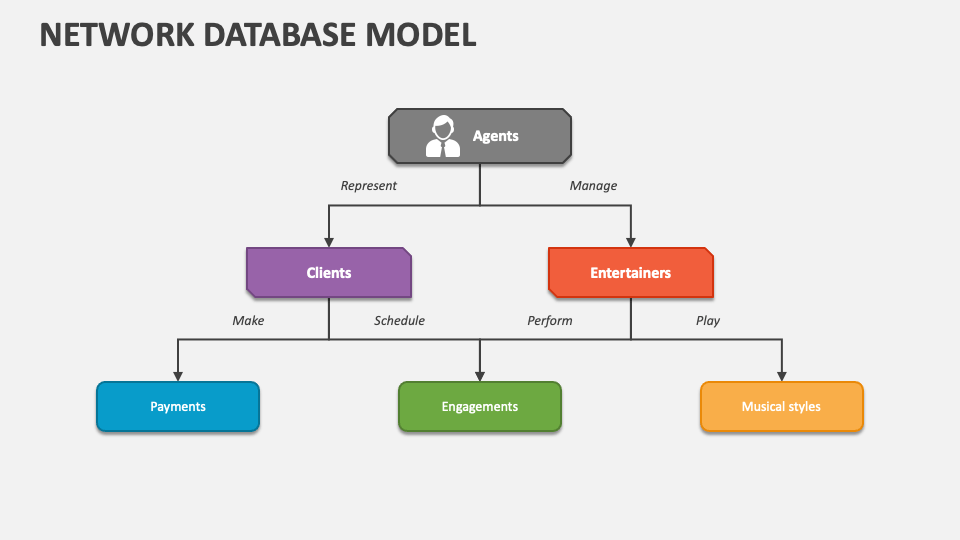

Extends hierarchical models by allowing many-to-many relationships.
✨ Features:
- Flexible relationships
- Complex connections
📌 Example:
Airline reservation systems ✈️
📦 Object-Oriented Data Model




Stores data as objects like in programming languages.
✨ Features:
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Reusability
📌 Example:
Multimedia and CAD applications 🎨
☁️ NoSQL Data Models
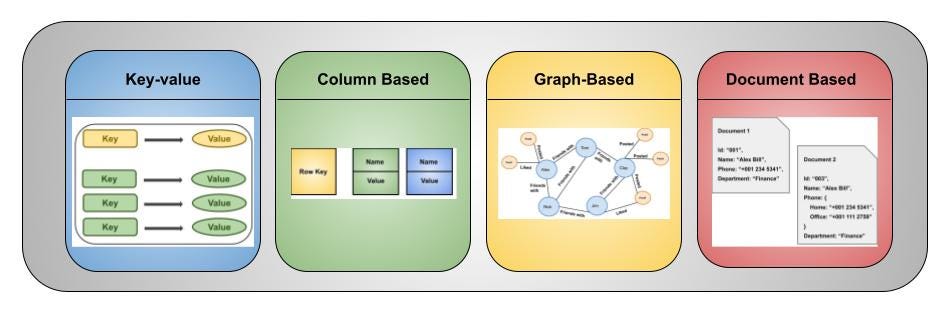



NoSQL supports flexible and scalable data storage.
Popular tools:
- MongoDB (Document)
- Redis (Key-Value)
- Neo4j (Graph)
✨ Features:
- Schema flexibility
- Horizontal scalability
- High performance
📌 Use Case:
Big data and real-time analytics 📈
📚 Core Data Modeling Concepts
🔑 Entities & Attributes
Objects and their properties.
🔗 Relationships
Connections between entities.
📐 Normalization
Organizing data to reduce redundancy.
🛡️ Constraints
Rules ensuring data integrity.
📊 Cardinality
Defines relationship quantities (1:1, 1:N, N:M).
🧭 Principles of Good Data Modeling
✅ Simplicity – Keep models understandable ✅ Scalability – Support future growth ✅ Integrity – Ensure accurate data ✅ Performance – Optimize access speed ✅ Consistency – Maintain uniform structure
🛠️ Popular Data Modeling Tools
- ER/Studio
- IBM InfoSphere Data Architect
- SAP PowerDesigner
These tools help design, visualize, and maintain complex data structures efficiently.
🌟 Real-World Example: E-Commerce Data Model
An online store might include:
- Users 👤
- Products 🛒
- Orders 📦
- Payments 💳
Relationships ensure seamless interaction between buying and selling processes.
💡 Daily Applications of Data Models
Data models power:
📱 Social media apps 🏦 Banking systems 🛍️ E-commerce platforms 🏥 Healthcare systems 🎮 Gaming platforms
Every organized digital system relies on data modeling!
🎯 Final Thoughts
Data models are the foundation of modern software systems. Mastering them improves your ability to design scalable and maintainable applications.
✨ “Good data modeling is the art of balancing structure and flexibility.”
Understanding these concepts equips you to build smarter databases and better software. 🚀
© Lakhveer Singh Rajput - Blogs. All Rights Reserved.

